

We conclude that DOT-A is a promising diagnostic instrument, and its economy and direct comparability to the Wechsler Digit spans and high sensitivity for patient populations make it especially well-suited for assessment in clinical practice. How can capacity in the STM be assessed Using the digit span technique which involves a list of numbers or letters, which participants have to recall immediately after.
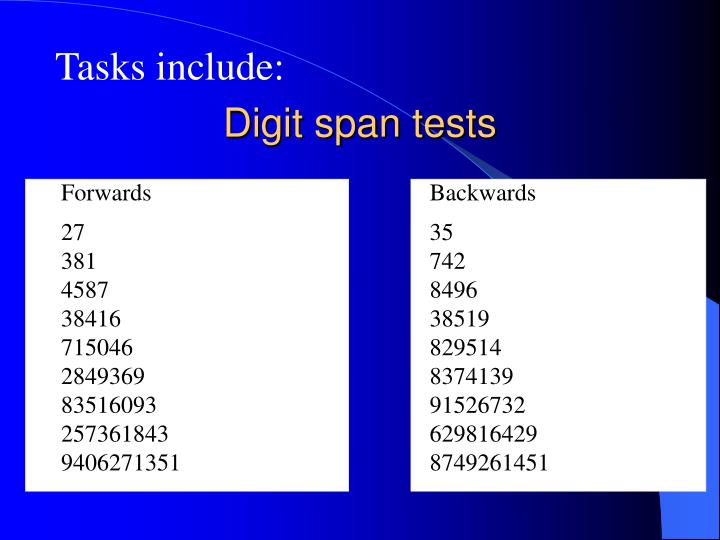
Concurrent validity was confirmed by significant correlation with a well-established working memory test (two-back task). Parallel test and split-half correlations indicated sufficient reliability of the DOT-A. In Study 2, DOT-A performance was assessed in 50 healthy subjects carefully selected according to demographic criteria in order to ensure representativity. (DGS) Digit Span (DGS) is a measure of verbal short term and working memory that can be used in two formats, Forward Digit Span and Reverse Digit Span. digits in American English in 1.5 seconds hence the digit span of 7. This pattern was found to be particularly sensitive for patients with PD. 10 hours a week for 40 weeks engaging in digit span tasks. In comparison with matched controls, both patient groups showed reduced performance in DOT-A but not in Digit span performance. In Study 1, we investigated DOT-A performance in patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD) and patients with frontal lobe damage, as these groups often exhibit working memory impairments within the framework of executive dysfunctions. and Swedish) were tested for digit span with and without articulatory suppression. DIGIT SPAN TEST - BACKWARD Use a monotonic voice without inflections at the end Say the digits at a rate of 1 digit about every 1 sec. , was developed in analogy to the Digit spans. was using the central executive and digit span made use of the phonological loop. For this purpose, the Adaptive Digit Ordering Test (DOT-A), a new version of a digit ordering test introduced by Cooper et al. Memory traces in the auditory store decay in 1.5 -2 seconds but can be. In the face of ample experimental evidence on the importance of working memory capacity for everyday life, there is a growing need for measures suited for clinical assessment of working memory.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
